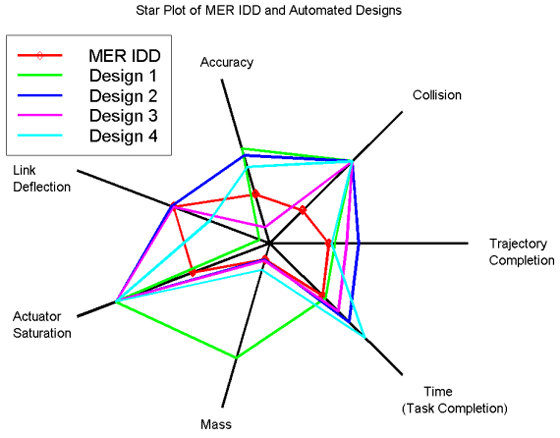
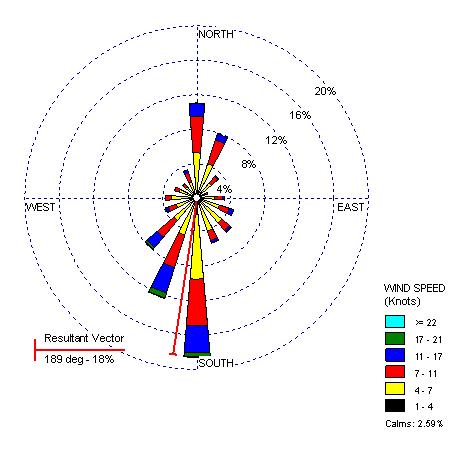
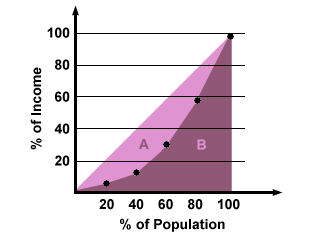
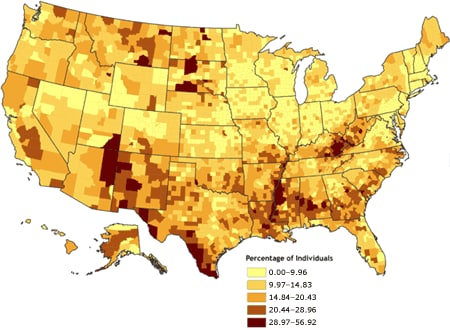
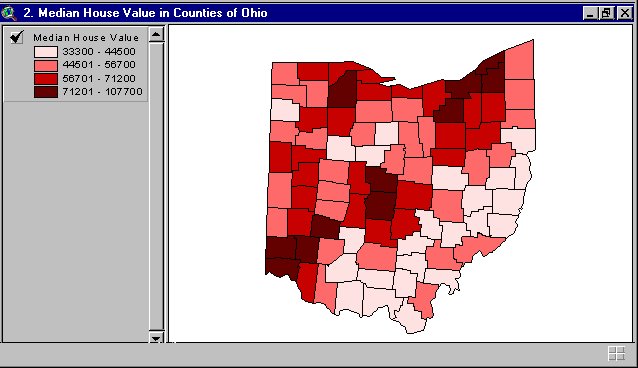
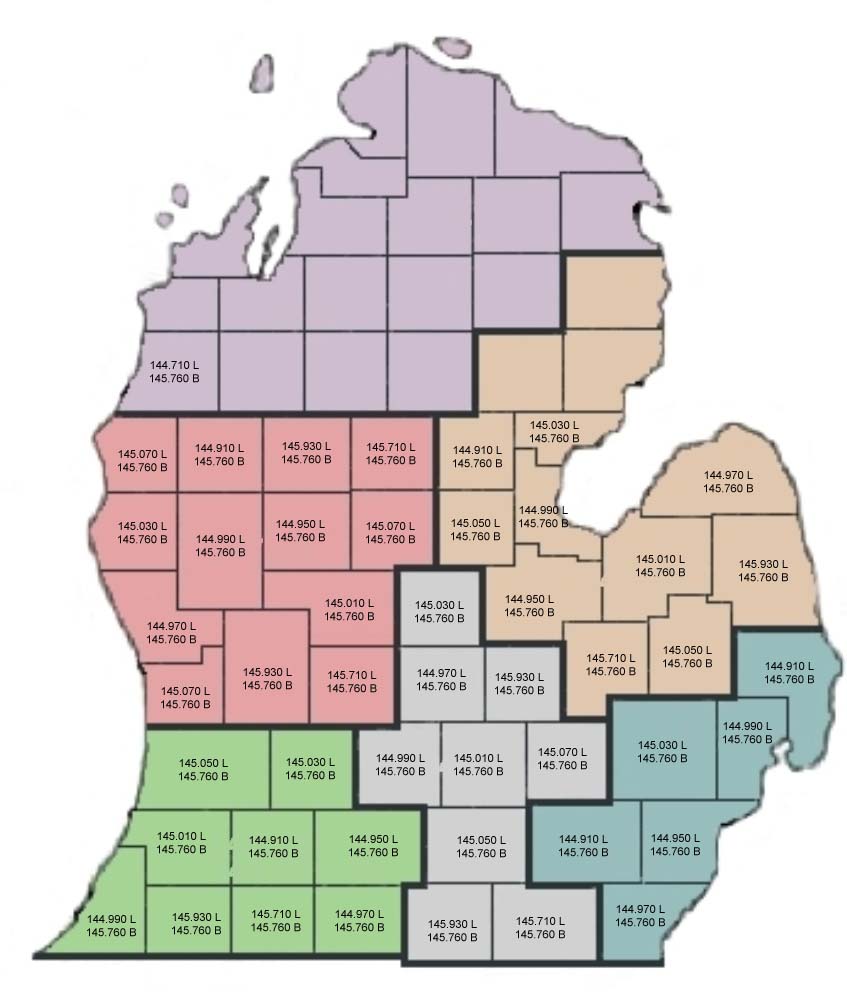
A Geography Information System (GIS) is a computer-based system made to display material referenced to the environment. GIS can be used for site remediation, natural resources management, groundwater modeling, vegetation mapping and more. GIS can also show different layers of data, as the one above is showing layers of monitoring wells, industries and population.